Is Ketamine Efficient for Regular and Atypical Melancholy?

Source: JerzyGorecki/Pixabay
Ketamine for despair
Ketamine is an anesthetic, a sedative, and a painkiller. Ketamine has been applied to deal with lots of actual physical and mental wellbeing problems, this sort of as serious ache, nervousness, article-traumatic worry condition (PTSD), and despair. For occasion, a type of ketamine referred to as esketamine (Spravato), administered as a nasal spray, was not long ago accepted by the US Foodstuff and Drug Administration (Fda) to handle cure-resistant despair.
An report by Park and colleagues at the Countrywide Institute of Psychological Health and fitness (NIMH), released in the November difficulty of Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, explored if ketamine is efficient in the treatment method of both common and atypical depressive signs.
Common despair and atypical melancholy
Ahead of describing the conclusions of the analyze, let me demonstrate the variance involving normal and atypical despair.
Common signs and symptoms of common depression (sometimes known as melancholic despair) are fat reduction, decreased sleep and appetite, and notably, an absence of temper reactivity. Temper reactivity implies the potential to truly feel greater, temporarily, in reaction to positive occurrences (e.g., obtaining a compliment, obtaining an desirable position offer you).
In contrast to standard depression, atypical melancholy is characterised by mood reactivity. In addition, as famous in the most up-to-date version of the Diagnostic and Statistical Guide of Psychological Diseases (DSM-5), atypical depression is also characterized by excessive sleeping, increased hunger or pounds attain, heaviness in arms and legs, and rejection sensitivity.
Despite its name, atypical melancholy is significantly from atypical. In other text, the behaviors previously mentioned are pretty popular signs of depression. So why are these indications named atypical depression?
It seems that the time period atypical melancholy “came into use in the late 1950s when psychiatrists discovered that for some frustrated people, tricyclic antidepressants ended up not effective,” unlike the MAOIs (monoamine oxidase inhibitors), which had been the only alternative at the time. These patients’ despair was unique from typical depression (i.e. remaining unhappy all the time). Thus, this style of depression was called atypical.
A pair of feedback about the drugs stated earlier mentioned. Neither tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., imipramine, brand identify Tofranil clomipramine, brand name name, Anafranil), nor MAOIs—the likes of tranylcypromine (Parnate), isocarboxazid (Marplan), and phenelzine (Nardil)—are approved as normally these times.
Why? Mainly because of possibly their facet results or comparatively limited efficiency. MAOIs, in particular, have really serious aspect effects and risky interactions with foods and drugs (e.g., selected cheeses, purple wine). These times, medical practitioners usually prescribe selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)—like fluoxetine (Prozac), sertraline (Zoloft), and others—regardless of the form of melancholy.
The analyze of ketamine’s results on melancholy
With all this in mind, permit us evaluation the research of ketamine for melancholy by Park et al.
The sample consisted of 68 individuals who took aspect in 1 of 3 NIMH investigations of the safety and efficacy of ketamine for the remedy of depression. These investigations ended up crossover trials that were being double-blind and placebo-controlled.
Scientists chose contributors who had a despair of at least reasonable severity (at first and just before just about every ketamine infusion), and who met the requirements for treatment method-resistant despair—depression that has not responded to an enough trial of one particular or much more antidepressants.
The ketamine cure was IV ketamine (ketamine infusion therapy): Ketamine (.5 mg/kg) was administered intravenously above 40 minutes. Individuals in the management group received saline placebo.
The ketamine and the placebo remedies have been administered in a random purchase, and the two therapies ended up separated by a two-7 days interval.
Melancholy was evaluated applying the Montgomery-Asberg Depression Ranking Scale (MADRS). Score scales have been administered multiple moments (e.g., right before, through, and just after infusions).
To measure regular/melancholic melancholy, the scientists applied 5 things measuring “apparent disappointment,” “inner rigidity,” “lassitude,” “inability to sense,” and “pessimistic feelings.”
To measure atypical signs and symptoms, the Scale for Atypical Symptoms (SAS) was applied. The products bundled “social withdrawal, bodyweight obtain, amplified appetite, improved ingesting, carbohydrate craving, hypersomnia, fatiguability (or weighty emotion), and diurnal variation (afternoon or night slump).”
The conclusions: ketamine infusion improved despair
Evaluation of results showed the subsequent:
There had been “statistically substantial swift advancements in equally normal/melancholic and atypical depressive symptoms” in reaction to a solitary infusion of ketamine, compared to placebo, in people with therapy-resistant depression with key depressive dysfunction or bipolar depression.
One particular day immediately after the infusion, ketamine seemed to deliver larger outcome measurements for indications of typical despair. However, by Day 3, the effect measurements for equally standard and atypical indications were being equivalent. See Determine 1.
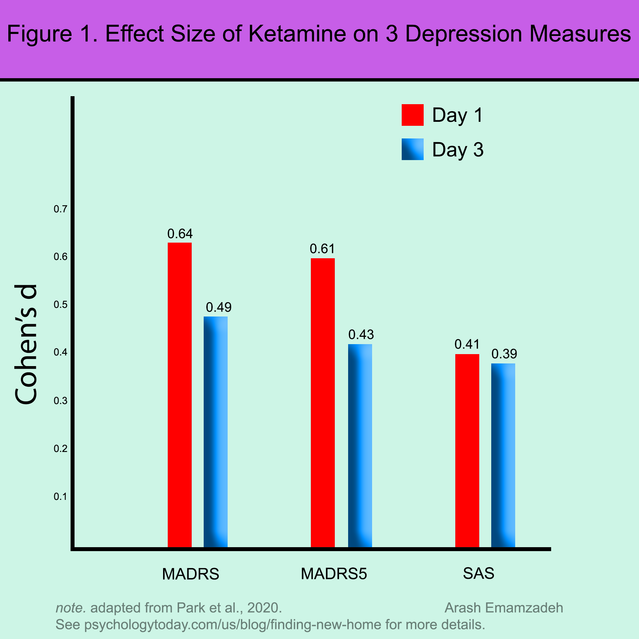
Source: Arash Emamzadeh (tailored from Park et al., 2020)
The steadiness of the influence sizing for atypical symptoms at Day 1 and Day 3 indicates ketamine shares similarities with MAOIs and can deal with each common and atypical signs of melancholy.
Having said that, the melancholic signs appeared much more responsive to ketamine earlier (on Working day 1, when compared to Day 3). The factors for this are not crystal clear.
Different mechanisms may possibly be dependable for how ketamine infusions affect typical and atypical signs. For instance, as the authors observe, “The inflammatory and immunometabolic procedures that hypothetically underlie the atypical symptom dimension may perhaps be a lot more resistant to ketamine’s rapid effects at Working day 1.”
As for ketamine’s effects on certain signs, it looks ketamine had the largest influence on the following normal and atypical symptoms:
- Normal: Sadness, lassitude, pessimism, and lack of ability to experience.
- Atypical: Social withdrawal, carbohydrate craving, and susceptibility to exhaustion.
Ketamine experienced considerably less of an impact on snooze and hunger, while it may perhaps be that three days were not enough time to see sizeable modifications in these regions.