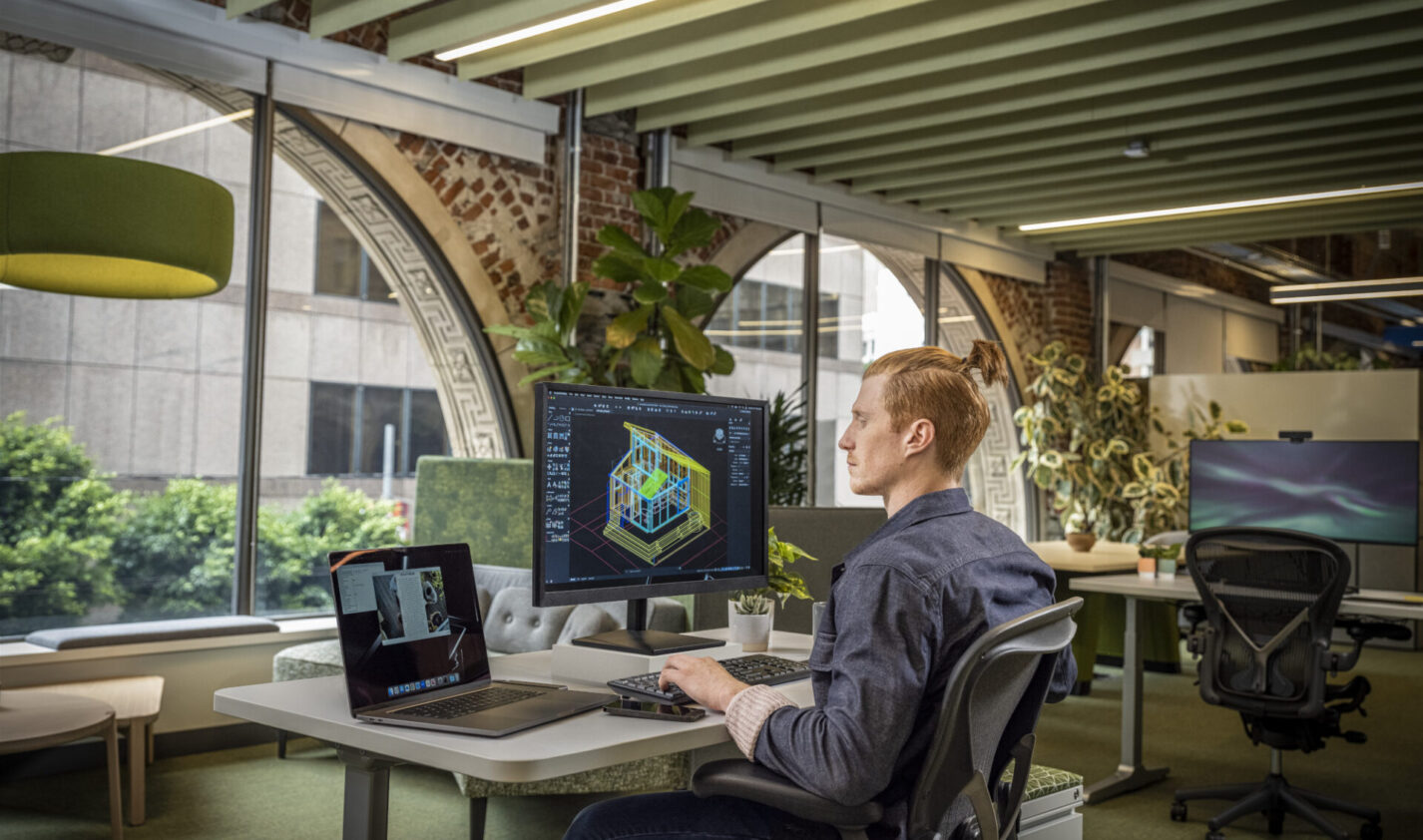
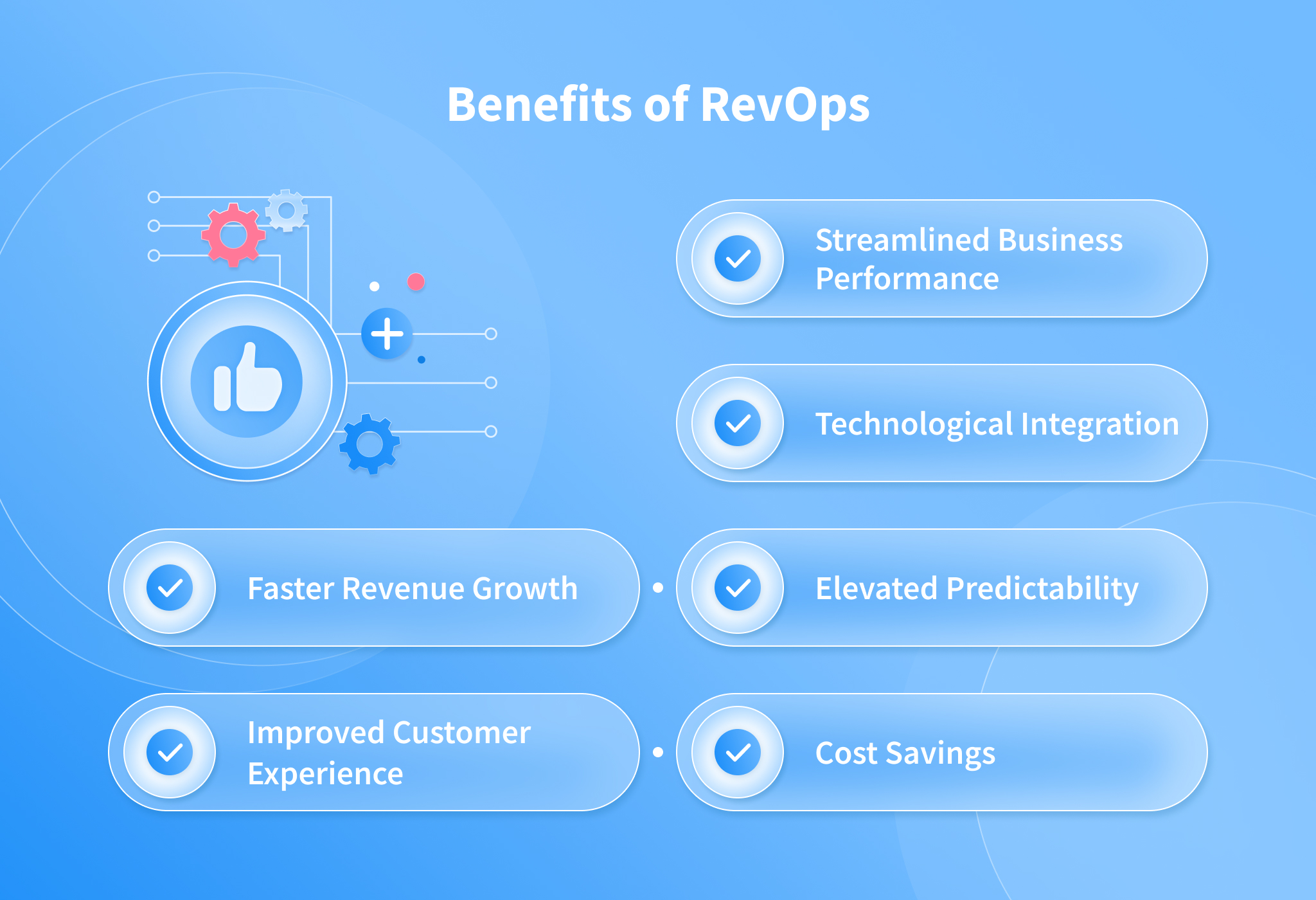
On factory flooring, a chime and flashing light to sustain distance
By Christopher F. Schuetze, The New York Moments Organization
BERLIN — The 2019-20 Countrywide Basketball Affiliation season was suspended for about 140 times right after a player tested positive for the coronavirus. But after enjoy resumed in late July, no other players tested optimistic.
The league was ready to evade the virus by requiring teams to dwell and perform their video games in an isolated place known as the Bubble, at the shut Disney Environment vacation resort in Florida.
But a compact piece of know-how also played a part: a wristband that gamers, coaches and trainers could put on off the courtroom, and that was expected for reporters covering the teams. A tiny electronic chip in the band enforces social distancing by issuing a warning — by light and audio — when wearers get too close to just one yet another for much too long off. The bands have been picked up by the Nationwide Soccer League, the Pacific-12 school conference and other sports activities leagues about the entire world.
The Munich startup behind the NBA’s wristbands, Kinexon, is content with the publicity of assisting protect against top athletes from catching the virus, even as these kinds of devices raise privacy considerations. Now it is wanting towards broader arenas: manufacturing unit manufacturing strains, warehouses and logistics facilities exactly where hundreds of thousands of people go on to get the job done inspite of the pandemic.
One of the businesses functioning with Kinexon is Henkel, a worldwide industrial and family chemical company based mostly in Germany. When the coronavirus infected about a dozen staff in Henkel’s plant in Serbia very last spring, the two-7 days shutdown that followed value hundreds of thousands of dollars in lost income, stated Wolfgang Weber, a senior manager for Henkel.
Henkel was presently screening an earlier model of Kinexon’s wearable tech, created to avert collisions among forklifts and staff on superior-targeted traffic factory floors. The system’s sensors would instantly halt a forklift if it acquired too near to a worker.
After the outbreak at the Serbian plant and inside weeks of the very first wave of pandemic lockdowns, Kinexon made available Henkel a probability to examination a variation of that technological know-how, named SafeZone. Its 50 percent-ounce sensor, worn on the wrist like a look at or close to the neck on a lanyard or on a badge, makes a chime and flashes when a further sensor is within just a prescribed length for a established period of time. Henkel agreed to give it a check out.
Testing the devices in genuine life was essential to Kinexon.

Anna Liminowicz, The New York Periods)
SafeZone sensors at the Henkel plant in Raciborz, Poland, on Oct. 8, 2020. Businesses like Henkel, a massive German chemical company, are seeking wearable sensors to protect against virus outbreaks amongst staff. (Anna Liminowicz/The New York Times)
“What’s crucial in this is not only to have the know-how working in a lab — what’s essential now is to be equipped to carry the engineering to in which individuals want it,” reported Oliver Trinchera, who co-started Kinexon in 2012 and is just one of its administrators, “be it on the manufacturing unit ground or on the sporting activities pitch.”
Henkel tested the program on the full team of its plant in Raciborz, Poland, a big facility on the southern outskirts of a medieval coal town, where 250 men and women function three shifts a day making and packaging powdered and liquid detergent for Central Europe.
The sensors have been programmed to go off when two people have been in 1.5 meters, approximately 6 ft, of each individual other for more than 5 seconds.
The sensors measure distance using extremely-broadband signals, which Kinexon says are additional correct and use far a lot less electricity than Bluetooth signals, the other technology typically observed in coronavirus tracing applications.
The workers use the sensors all through their shift, reminding them to maintain their length even all through lunch in the canteens.
Adrian Wycisk, the plant’s supervisor, in contrast the sensors’ chimes to the warn in automobiles when men and women have not place on their seat belts.
“It ultimately variations the habits in drivers,” he explained, adding that he has viewed a marked advancement in workers’ preserving a safe and sound length.
The method merchants, for a number of months, information on when a employee was near other workers — a perhaps helpful software for tracing interactions if a worker becomes contaminated, but one particular that raises worries about management’s retaining tabs on a worker’s actions all shift extended.
Henkel explained that it gave only a tiny amount of senior supervisors access to the information, and that the enterprise experienced dispersed pamphlets explaining to employees that the badges would never be made use of to keep track of their movements. The data information which personnel interacted, not exactly where the interaction took spot. Wycisk claimed Henkel had vowed to retrieve the information only if a coronavirus infection desired to be traced.
The German union that represents Henkel workers declined to remark about the technological innovation.
In the prolonged run, the technology could also support Henkel reconfigure some of its creation procedures to prevent close call, Weber claimed.
Kinexon has marketed the technological know-how to a range of nicely-known German producing and cargo businesses — the tire maker Continental and the logistics big DB Schenker ended up early adopters. Kinexon claimed that it has worked with U.S. companies, but that it was contractually obligated not to launch their names.
In general, the company explained it is providing the technology to more than 200 organizations worldwide. It estimates its badges have prevented 1.5 million contacts a working day, a tough number to validate. The sensors are priced concerning $100 and $200 just about every.
The 6-week take a look at in Raciborz, throughout which no worker analyzed positive, persuaded Henkel to roll out the know-how in its cleansing-chemical compounds creation web sites in excess of the future yr. How lots of of the company’s 52,000 personnel throughout the world finally use the engineering relies upon on how extended the pandemic continues.
If the vaccines are prosperous and the pandemic is defeat sometime this year, Weber explained, he options to the reuse the sensors for their original intent: to prevent collisions in between employees and forklifts. The point that such plans would require much less badges than Henkel getting is not a problem.
“I would still say that it is a achievements,” he claimed.