| Jan 20, 2021 |
|
|
|
(Nanowerk News) Roofs are not the only suited places for setting up photovoltaic modules to crank out electrical energy from the suns rays. Facades could also engage in a significantly additional considerable role in Germanys energy changeover towards renewables as very well as aiding to reduce land intake for electrical power parks. Together with the Fraunhofer ISE, the Leibniz Institute of Ecological City and Regional Development has calculated the prospective spot of Germanys setting up facades for the installation of PV techniques. It is two times as big as that of roofs.
|
|
They printed their findings in the journal Reworking Cities (“Die vertikale Stadt als solare Energiequelle? Theoretische Flächenpotenziale für bauwerksintegrierte Photovoltaik und Abschätzung der solaren Einstrahlung”).
|
|
Photo voltaic panels have lengthy been a popular sight on German rooftops. In numerous cities and towns, solar cadastres deliver info about the ability for producing power from this sort of roof-based techniques. Regional authorities even offer incentives to motivate inhabitants to set up PV modules on their roofs. But what about the facades of structures? How significantly useful floor region do they present for the era of renewable power?
|
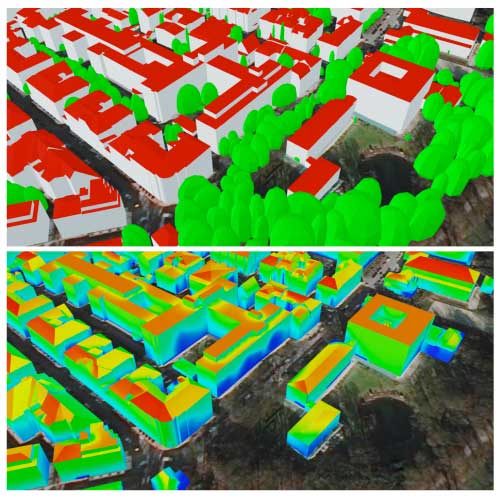 |
| Smaller-scale analyses of the solar likely dont just take into account the buildings and their surfaces in the modelling but also the speedy environment. Below we evidently see the impression on the possible electricity yield when buildings are shaded by close by trees. Blue stands for very low strength yield, red for substantial generate. (Resource: Behnisch et al./IOER, knowledge basis: essential geodata, Bavarian surveying administration 2019)
|
A probable region of 12,000 sq. kilometres at minimum in idea
|
|
“To accomplish the German governments purpose of local climate neutrality in the building stock by 2050, it will not be adequate just to set up photo voltaic programs on all suitable roofs in Germany,” explains Dr Martin Behnisch of the Leibniz Institute of Ecological City and Regional Advancement (IOER).
|
|
Determined to investigate an additional option, the IOER investigated the solar ability of facades. Working in close cooperation with scientific partners these kinds of as the Fraunhofer Institute for Photo voltaic Strength Techniques (ISE), the Weimar Institute of Applied Design (IAB), the Chair of Geoinformatics at the Technological University of Munich as effectively as with enterprise associates from the solar electrical power market, the ensuing Typical BIPV undertaking was funded by the Federal Ministry for Financial Affairs and Strength.
|
|
Centered on formal geodata, the team led by Martin Behnisch of the IOER investigated the opportunity location available by Germanys developing facades for putting in setting up-built-in photovoltaics (BIPV).
|
|
The findings are amazing. As Dr Martin Behnisch describes: “The opportunity area is estimated to be all-around 12,000 square kilometres of facade in contrast to just less than 6,000 sq. kilometres of roofing.” This indicates that building facades give about two times the capacity for photovoltaic modules as roofs, equalling about half the territory of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. However Behnisch is cautious: “We have to emphasise that these are nevertheless just theoretical values.”
|
Calculations based mostly on national geodata
|
|
The outcomes are nevertheless considerably tentative as they are centered on knowledge that, in section, considerably simplifies the actual-environment circumstances. For their examine, the scientists analysed a 3D product created by the Federal Agency for Cartography and Geodesy (BKG) which delivers details on Germanys full stock of properties. Just about every home is modelled as a easy block with a flat roof.
|
|
Detailed roof styles and resulting gable partitions, windows, doors or projecting components such as balconies and other features are not mirrored in the constructing design. Even further, the design does not consider no matter if a developing is of historic benefit or possesses a precious façade style. On the other hand, the analysis teams estimate does disregard properties whose facades are touching and consequently are unsuitable for the installation of photovoltaics.
|
|
In addition, detailed analyses were carried out on 3 focus on regions, namely the towns of Munich, Freiburg and Dresden, as effectively as on a nationwide sample of 100,000 structures.
|
|
In shut cooperation with a staff led by Prof. Thomas H. Kolbe from the Specialized University of Munich, IOER scientists modelled and visualised the photo voltaic radiation falling on all roof and facade surfaces in buy to specifically figure out the little-scale likely generate of photo voltaic electrical power. To do this, the staff not only built use of comprehensive creating versions that includes specific roof layouts the calculations also took into account the surroundings these kinds of as trees and the shade they forged or shadows brought on by other properties as effectively as the neighborhood topography and any close by mountains.
|
Enhanced setting up of photovoltaics on buildings
|
|
The effects are numerous visualisations of the potential surface area location for PV modules and prospective solar electricity yields in Germany. For illustration, the spatial distribution of probable parts shows us that the potential for setting up-integrated photovoltaic modules is specifically significant in destinations with dense populations. This is the circumstance, for instance, in the Rhine-Primary, Rhine-Neckar and Rhine-Ruhr conurbations, as perfectly as in the urban centres of Berlin, Hamburg, Bremen, Munich or the Saxon city triangle of Dresden-Leipzig-Chemnitz.
|
|
When concrete making types are regarded in the modelling of solar vitality yields, it becomes distinct that the facades of significant buildings these types of as manufacturing halls, academic institutions or community properties are particularly suited for putting in PV systems. But in accordance to Martin Behnisch: “Large residential complexes this sort of as significant-rise buildings are also superior locations for the installation of photovoltaics.”
|
|
The IOER task workforce sees their findings as a to start with stage in direction of the enhanced preparing of power technology on structures. Martin Behnisch again: “Our information nevertheless has to be specified for particular person web sites by way of far more precise analyses. But it does give an impression of the wonderful likely that can be tapped by making-integrated photovoltaics. These are critical beginning factors, especially with a perspective to conference targets for lowered CO2 emissions.” In view of the transport revolution away from fossil fuels and the issues of e-mobility, it helps make sense for us to produce more clear strength in metropolitan areas. On top of that, there are also benefits for environmental safety. “Every photovoltaic module that we put in on a residence facade will help to preserve character and precious soil by averting the development of big photovoltaic electric power stations.”
|
History
|
|
In the Regular BIPV job (Advancement of a Prefabricated Common BIPV Facade for Selected Building Categories in Germany), the challenge associates identified suitable building categories that could be equipped with prefabricated, standardised BIPV façade. Further, they implemented an preliminary exemplary up grade. On the 1 hand, the purpose was to detect suitable building varieties with large facades for photo voltaic electrical power generation. On the other hand, photovoltaic facade aspects had been made in the system of the job with a price tag-helpful style for mass output and which can be simply assembled/set up and are adequately attractive.
|
|
The challenge partners had been the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Electrical power Techniques (ISE) (guide partner) U. I. Lapp GmbH, Stuttgart Good Photo voltaic Electricity GmbH, Schwäbisch Corridor IWE Innovativer Werkstoffeinsatz GmbH & Co. KG, Greifswald the IAB Weimar Institute for Applied Development gGmbH GES Gebäude- und Energiesysteme GmbH, Korbußen, ARMOR photo voltaic ability films GmbH, Kitzingen as perfectly as the Leibniz Institute of Ecological Urban and Regional Improvement (IOER), which, in shut cooperation with the Chair for Geoinformatics at the Specialized College of Munich (Prof. Thomas H. Kolbe), was dependable for the geodata-centered investigation of the potential places and the analyses of solar radiation.
|

